Tutorial
Concept
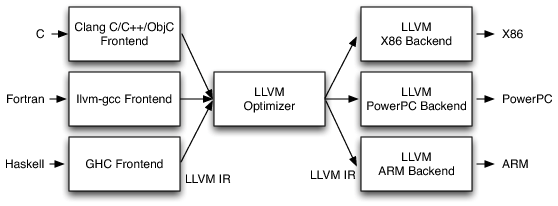
LLVM Architecture Overview. Reference: The Architecture of Open Source Applications (Volume 1) LLVM
-
LLVM Tablegen is a language used in LLVM to help configure target-specific attributes easier. The Tablegen language files will be suffix with
.td(target description). At the build time, the*.tdfile will be compiled to cpp files first, and link with other cpp sources. You may want to checkout the document for more information. It will be used for:- Defining new RISC-V extension
- Defining instruction format
- Defining CSRs
- Defining intrinsic functions
- Defining DAG for pattern matching
- etc.
-
Where to find the file to modify?
- C/C++ frontend:
clang - Compiler backend:
llvm- Target related:
llvm/*/Target(*could beincludeorlib)
- Target related:
- C/C++ frontend:
Adding new features
Defining new RISC-V extension
- File to modify:
llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVFeatures - Define a new
RISCVExtensionrecord - Define a new
Predicatesrecord- So that you could check if a specific extension is enabled in your cpp files or other Tablegen files.
- Currently, FORMOSA has two extensions:
xformosapriandxformosabar - If you have a processor defined in LLVM, you could specifies its extension at
llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVProcessors.td. For example, whe using-mcpu=formosa-gpgpuflag, the compiler will know that ths ISA string isrv64im_zicsr_zifencei_zdinx_zicond_xformosapri_xformosabar
Defining new custom instructions
- File to modify:
llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVInstrInfo*.td - Define records of your instruction, which should be the record of the
optype class. For example, for anRtype instruction, you should define record ofRVInstRclass and for anItype instruction, you should define record ofRVInstrI- Defining the
funct3,funct7,mnemonic
- Defining the
- You could set the attribute for a class or a record
- The instruction will be enabled when some predicates (extensions) are enabled
- Whether the instruction will have load/store behavior or has any side effects
- This is very important for compiler optimization, examine your instruction and set it correctly!
- Currently, all of FORMOSA custom instructions are defined in
llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVInstrInfoXFormosa.td
Defining new CSRs
If you have a new custom CSR and you want your compiler to recognize it when you are writing csrr, csrw instructions, you will have to add those to llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVSystemOperands.td
The definition should be SysReg record, where you need to specify the name and address for the register.
Defining new instrinsic functions
Intrinsic functions are functions that are built-in in the compiler. We need to modify both front-end and back-end of the compiler to make it works.
- Add built-in function in
clang- File to modify:
clang/include/clang/Basic/BuiltinsRISCV.td - Define records of your built-in functions, the record should be of type
RISCVBuiltin - You will have to specify the return type and argument types of each built-in functions
- For example:
def fsa_pri_set: RISCVBuiltin<"void(uint64_t)">takes oneuint64_targument and returnsvoid
- For example:
- Defining a record here would automatically generate function named
__builtin_riscv_<your record name>
- File to modify:
-
Add intrinsic records
- File to modify:
llvm/include/llvm/IR/IntrinsicsRISCVXFormosa.td - Here, you have to define a intrinsic record for your built-in function defined previously
- The record should be of type
ClangBuiltin<"your_bulitin_fn_name">andIntrinsic - Note that you will have to match the argument type and return type for your built-in functions
- For example: the
int_riscv_fsa_pri_setinheritsIntrinsic<[], [llvm_i64_ty], [IntrNoMem, ...]>, the first argument ofIntrinsicis the return type void, the second argument is the types of builtin function argument list, and the third argument is the properties for the instrinsic node.- The properties should be set correctly! See
llvm/include/llvm/IR/Intrinsics.tdfor possible properties and its definitions.
- The properties should be set correctly! See
- For example: the
- File to modify:
-
Pattern matching for a instrinsic function If you want to simply lower your intrinsic function to your custom instruction, you will have to define a pattern matching from the intrinsic node to the instruction node.
- File to modify:
llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVInstrInfo*.tdThe record will be something like the following format: def: Pat<(source DAG), (target DAG)>- The DAG in Tablegen will be described with the combination of parenthesis
- source DAG: the intrinsic node
- target DAG: could be anything, could be a single instruction node or combination of instruction nodes
DAG Node
DAG Node: the basic form is (operator, operand1, operand2). For example (add x, y)
- File to modify:
Writing a new LLVM pass
LLVM pass is to either analyze or transform your program for optimization. The optimization is global optmiation, that is, the pass is perform on functions. The passes could be done either at IR level or machine IR (MIR) level. For FORMOSA, we done our passes in MIR level.
- Define the create and initialize functions
You sould define two functions in
llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCV.hFunctionPass *createRISCV*Pass()Return your implementation classvoid initializeRISCV*Pass(PassRegistry &)
- Then, you should create a class that inherits
MachineFunctionPassand implement your pass algorithm (Example link) The class should override the following functions:void intialize(MachineFunction &MF)Initialize and get the information you need. For example, the instruction info or the register info of your target.bool runOnMachineFunction(MachineFunction &MF)Implement your algorithm in the this function. If it is an analysis pass and does not modify the original MIR, returnfalse. Otherwise, if any modification is made, returntrue.- If the pass is depend on other pases, you should specify the dependencies in the macro
INITIALIZE_PASS_DEPENDENCY. Therefore, the dependency pass will be run before your pass is run.
- Register your pass
- File to modify:
llvm/lib/RISCV/RISCVTargetMachine.cpp - You should add your initialization function defined in
RISCV.htoLLVMIntializeRISCVTarget() - Determine when you want your pass to work. For example, if your want your pass to work lastly, you could consider adding
addPass(createRISCV*Pass())at theRISCVPassConfig::addPreEmitPass(). So that the pass will be run before emission.
- File to modify:
IR level optimization
If you want to add a IR level optimization pass, you may want to take a look at llvm/lib/Analysis directory for the analysis passes and llvm/lib/Transforms for the transformation passes.